| BIOCHEMICAL DEFICIENCY  DIAGNOSIS Gene  |
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS Neurological  |
THERAPY Dietary Protein  |
THERAPY Treatment  |
| General Resources |
Literature Resources |
Patient Resources |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
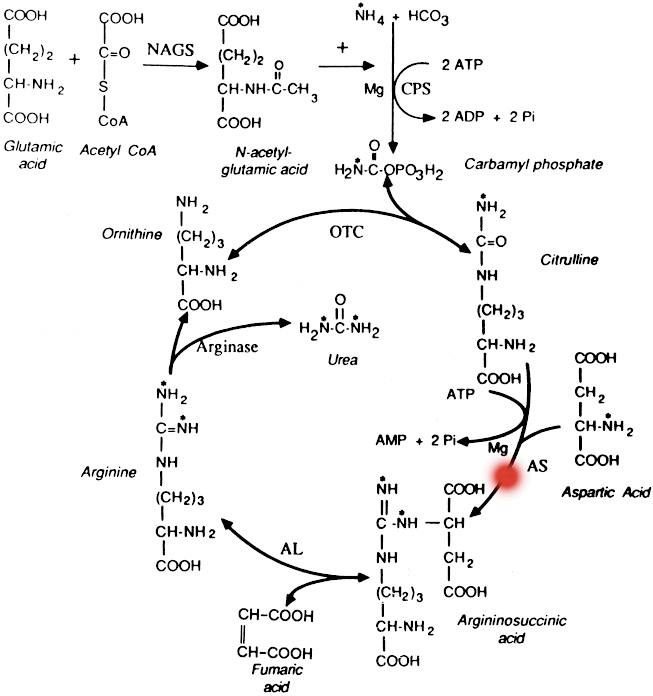
Late-Onset Citrullinemia
is an inherited disorder that causes ammonia and other toxic substances to accumulate in the blood. This condition, also known as classic citrullinemia, belongs to a class of genetic diseases called urea cycle disorders. In most cases, the condition becomes evident in the first few days of life. Affected infants typically appear normal at birth, but as ammonia builds up in the body they experience a progressive lack of energy (lethargy), poor feeding, vomiting, seizures, and loss of consciousness. The late-onset form may be milder than that seen in the acute neonatal form, for unknown reasons. The episodes of hyperammonemia are similar to those seen in the acute neonatal form, but the initial neurologic findings may be more subtle because of the older age of the affected individuals; all patients develop some form of intellectual disability.(Source: Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center)